External Commercial Borrowing is the loan/ debt/ borrowings taken by an eligible entity in India for commercial purpose, externally i.e. from any recognized entity outside India. The ECBs are governed by the regulations of RBI under Master Direction – External Commercial Borrowings, Trade Credits and Structured Obligations (Master Direction) and Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA).
WHO IS THIS FOR?
A firm looking for commercial loans [in the form of bank loans, buyer’s credit, supplier’s credit, secularized instruments (e.g. floating rate notes and fixed-rate bonds), which go to ECB that are availed from non-resident lenders with a minimum average maturity of 3 years.
HOW DO I SIGN UP?
Your business/financial analysis report, financial model, valuation, pitch book, or Information Memorandum will be compiled
NDA and mandate are signed on agreed terms after target companies/investors are reached out using a tailor made methodology.
OUR PROCESS
Borrowers may enter into loan agreements complying with the ECB guidelines for raising ECB under Automatic Route without the prior approval of the Reserve Bank. The borrower must obtain a Loan Registration Number (LRN) from the Reserve Bank of India before drawing down the ECB.
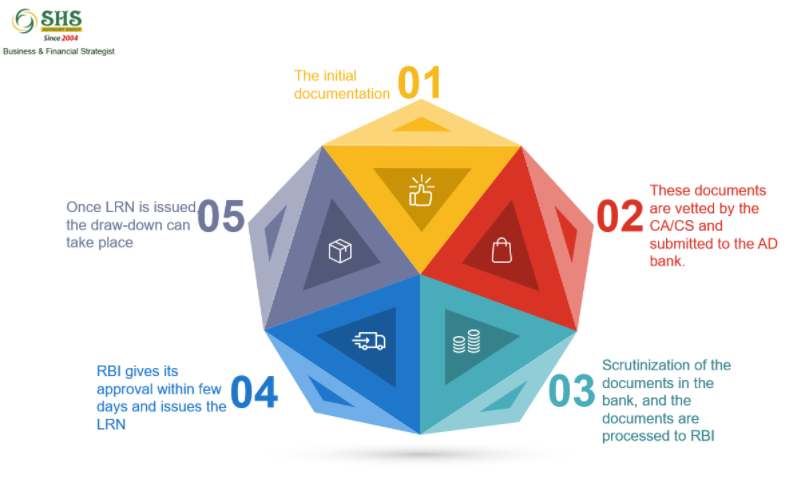
The initial documentation includes filling form ECB, making a loan agreement, making average maturity, repayment and interest payment schedule and request letter.
These documents need to be vetted by the CA/CS of the borrowing company and submitted to the AD bank.
Various departments scrutinize the documents in the bank, and once they find all facts okay, the documents are processed to RBI
Usually, under the automatic route, the RBI gives its approval within a few days and issues the LRN
Once LRN is issued, the draw-down can take place